π-Interactions between Cyclic Carbocations and Aromatics Cause Zeolite Deactivation in Methanol-to-Hydrocarbon Conversion
Date:2020/4/28 14:44:02 Views:Times
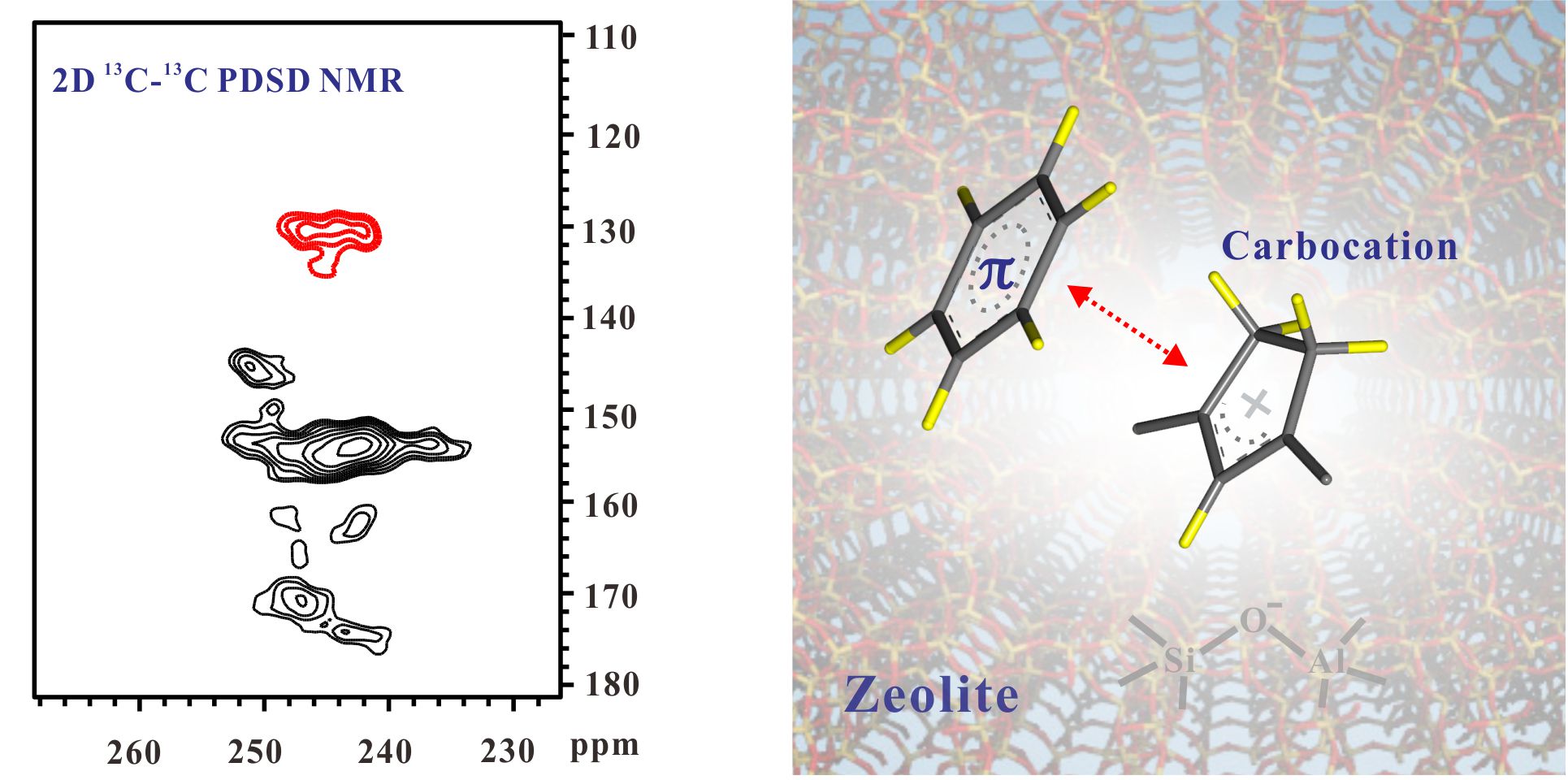
The understanding of catalyst deactivation represents one of the major challenges for the methanol-to-hydrocarbon (MTH) reaction over acidic zeolites. Here we report the critical role of intermolecular p-interactions in catalyst deactivation in the MTH reaction on zeolites H-SSZ-13 and HZSM-5. p-interaction-induced spatial proximities between cyclopentenyl cations and aromatics in the confined channels and/or cages of zeolites are revealed by two-dimensional solidstate NMR spectroscopy. The formation of naphtalene as a precursor to coke species is favored due to the reaction of aromatics with the nearby cyclopentenyl cations and correlates with both acid density and zeolite topology.
Link:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/anie.202000637



