Water-Induced Micro-Hydrophobic Effect Regulates Benzene Methylation in Zeolite
Date:2023/11/7 16:47:35 Views:Times
Abstract
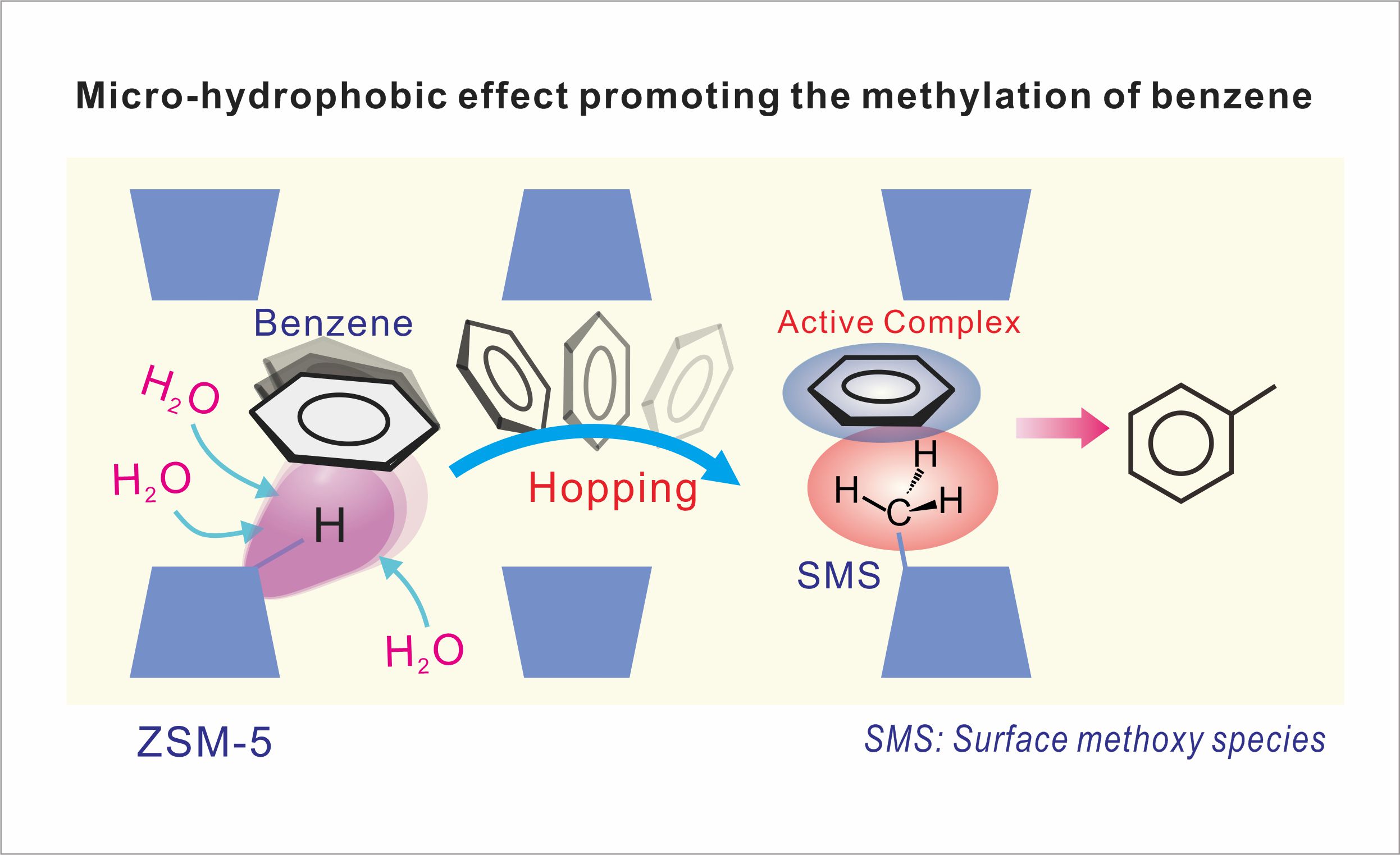
Water is a ubiquitous component in heterogeneous catalysis over zeolites and can significantly influence the catalyst performance. However, the detailed mechanism insights into zeolite-catalyzed reactions under microscale aqueous environment remain elusive. Here, using multiple dimensional solid-state NMR experiments coupled with ultrahigh magic angle spinning technique and theoretical simulations, we establish a fundamental understanding of the role of water in benzene methylation over ZSM-5 zeolite under water vapor conditions. We show that water competes with benzene for the active sites of zeolite and facilitates the bimolecular reaction mechanism. The growth of water clusters induces micro-hydrophobic effect in zeolite pores, which reorients benzene molecules and drives their interactions with surface methoxy species (SMS) on zeolite. We identify the formation and evolution of active benzene-SMS complexes in microscale aqueous environment and demonstrate that their accumulation in zeolite pores boosts benzene conversion and methylation.
Link:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.202313974



